Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized the AI landscape; however, their training process remains a significant challenge due to high costs and resource-intensive requirements. DeepSeek’s breakthrough with its R1 model, which claims to achieve a 95% reduction in training costs, offers an early glimpse into the future of low-cost, faster LLM training. LLM creators and tech companies are investing heavily in innovative solutions to reduce the time, financial costs, and environmental impact of training these models.
This post explores advancements in the industry and outlines primary approaches for customers leveraging LLMs across a set of scenarios.
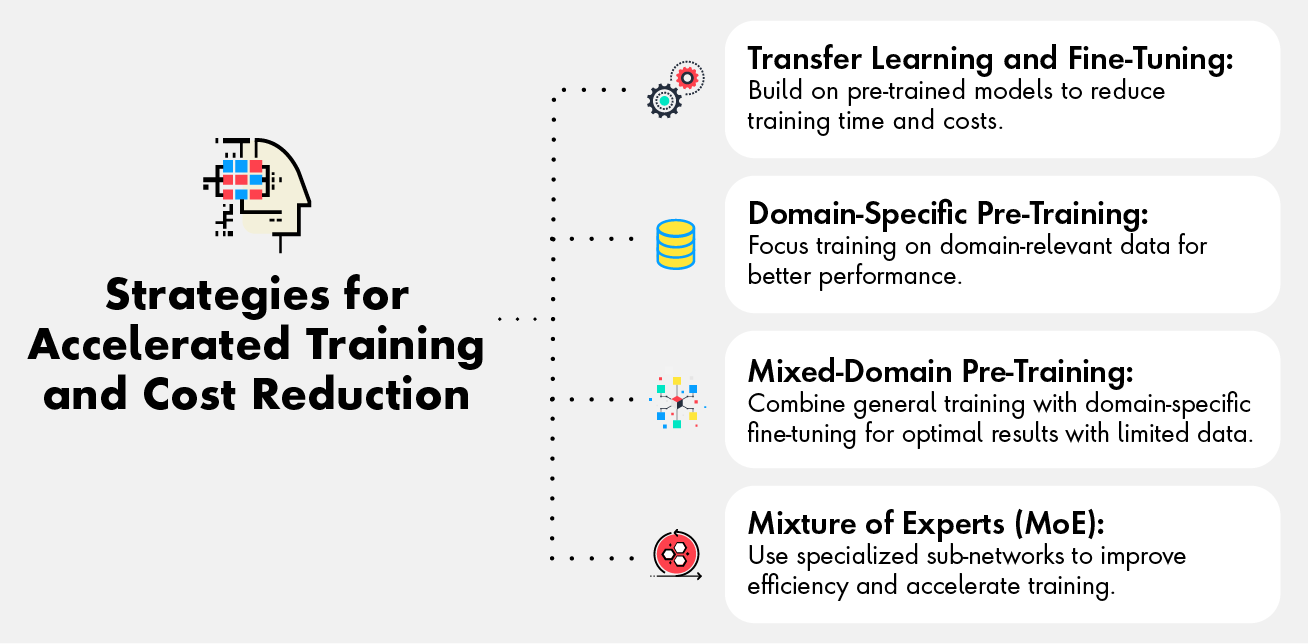
The key advancements here are around the following approaches:
- Hardware Innovations involving tweaking and streamlining of the training hardware, such as custom chips from Microsoft.
- Software optimization techniques with a focus on getting better training performance with existing hardware by ensuring effective memory utilization. Techniques such as Mixed precision training and Activation checkpointing have proven to be effective in this category.
- Distributed model training by either leveraging multiple GPUs in parallel to train and/or using data parallelism technique designed to optimize memory usage and scalability during the LLM training by leveraging libraries such as FSDP
- Optimized training frameworks such as Fast-LLM from ServiceNow, an open-source library developed for training models of all sizes employs a mix of the above techniques (mixed-precision, distributed training and hardware optimizations) to maximize throughput and minimize training time.
- In scenarios where a smaller model is a better fit, techniques like Knowledge distillation, where a smaller "student" model is trained to replicate the performance of a larger "teacher" model, can be effective. This allows the student model to benefit from the teacher's knowledge without the extensive computational resources required to train the larger model from scratch.
- Shift from traditional supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to reinforcement learning (RL)-first approach as used for DeepSeek-R1. Most large language models (LLMs) begin their training with supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to establish foundational knowledge. However, DeepSeek-R1-Zero deviated from this traditional approach by skipping the SFT stage entirely. Instead, it was trained exclusively using reinforcement learning (RL), allowing the model to independently develop advanced reasoning capabilities, such as chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning. This innovative RL-first strategy enabled the model to explore and refine its reasoning processes without relying on pre-labeled data.